Structure and Properties
Molecular sieves are crystalline, highly porous materials that belong to the class of alumina silicate. These crystals are characterized by a three-dimensional pore system with pores of precisely defined diameter. The corresponding crystallographic structure is formed by tetrahedra of (AlO4) and (SiO4). These tetrahedra are the basic building blocks for various molecular sieve structures, such as molecular sieve A and X, the most common commercial adsorbents.
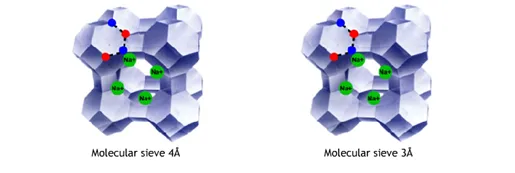
Due to the presence of alumina, the molecular sieves exhibit a negatively charged framework, which is counterbalanced by positive cations, resulting in a strong electrostatic field on the internal surface. These cations can be exchanged to fine-tune the pore size or the adsorption characteristics. For instance, the sodium form of zeolite A has a pore opening of approximately 4 Ångstrom (4 x 10^-10 m), called a 4A molecular sieve. If the sodium ion is exchanged with the larger potassium ion, the pore opening is reduced to approximately 3 Ångstrom (3A molecular sieve). An ion exchanged with calcium, where one calcium ion replaces two sodium ions, increases the pore opening to approximately 5 Ångstrom (5A molecular sieve). Ion exchange with other cations is sometimes used for particular separation purposes.
The pore opening of the sodium form of the molecular sieve X (13X) is approximately 8 Ångstrom.
The ability to adjust the pores to precisely determined uniform openings allows for molecules smaller than the pore diameter to be adsorbed while excluding larger molecules, hence the name “molecular sieve.” The different pore sizes of synthetic molecular sieves open up a wide range of possibilities in terms of “sieving” molecules of different sizes or shapes from gases and liquids.
Selective Adsorption of Water and Other Polar Substances The uptake of water or other species in the molecular sieve is called adsorption and functions on the basis of physisorption. The main driving force for adsorption is the highly polar surface within the pores. This unique characteristic distinguishes the molecular sieve from commercially available absorbents, enabling an extremely high adsorption capacity for water and other polar components even at very low concentrations. Additionally, the pore size plays a significant role in allowing or prohibiting the entrance of molecules to the pore system.
The adsorption on molecular sieves is therefore dependent on the following physical molecular properties:
- Size and Shape: Molecules larger than the pore opening of the molecular sieve cannot be adsorbed, while smaller molecules can.
- Molecular Polarity: Molecules with high polarity or polarizability can be adsorbed preferentially under identical conditions.
Activated Alumina Desiccant
Description: White bead, regular in particle size, smooth at surface, with high crushing strength and strong adsorption of moisture, not expanding and cracking after adsorbing water, original shape kept.
Odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, insoluble in water and alcohol.
Application
Widely used in oxygen making industry, textile industry, for gas drying in electronic industry. Used for air separation, in petroleum and chemical industries as drying and cleaning agent.
Specification:
| Item | Unit | Bead | ||||||
| Diameter | mm | 0.4-1.2 | 2-3 | 3-4 | 3-5 | 4-6 | 5-7 | 6-8 |
| SiO2 | ≥wt% | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Fe2O3 | ≤wt% | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Na2O | ≥g/ml | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| L.O.I. | ≤N/Pc | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Bulk Density | ≤wt% | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Surface | ≤wt% | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| Pore Volume | ≥ml/g | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 |
| Crushing Strength | ≥N/Pc | / | 60 | 100 | 130 | 160 | 180 | 200 |
AI2O3%= (100%- SiO2%- Fe2O3%- Na2O%- L.O.I.)
Molecular Sieve 3A
Description: A kind of potassium-sodium aluminosilicate, with crystal diameter of 3 angstroms (0.3nm).
Application
In deep desiccation of cracked petroleum gases, unsaturated hydrocarbons (such as ethylene, propylene, butadiene, acetylene).
Used for dehydration of benzene, toluene, xylene and other solvents (methanol, ethanol), and food grade CO2 gas.
Specification:
| Item | Unit | Bead | Pellet | ||
| Diameter | mm | 1.6-2.5 | 3-5 | 1/16′ | 1/8′ |
| Static Water Adsorption | ≥wt% | 20.5 | 20.5 | 20.5 | 20.5 |
| CO2 Adsorption | ≤wt% | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Bulk Density | ≥g/ml | 0.70 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.66 |
| Crushing Strength | ≤N/Pc | 25 | 75 | 30 | 70 |
| Attrition Rate | ≤wt% | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Package Moisture | ≤wt% | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
Molecular Sieve 4A
Description: A kind of sodium aluminosilicate, with crystal diameter of 4 angstroms (0.4nm).
Application
It is mainly used for desiccation of gases, natural gas, alkane and other organic solvents. Used for refining and purification of gases and liquids, such as argon.
Drying for drug packaging, electronic components, etc.
Specification:
| Item | Unit | Bead | Pellet | ||
| Diameter | mm | 1.6-2.5 | 3-5 | 1/16′ | 1/8′ |
| Static Water Adsorption | ≥wt% | 21.5 | 21.5 | 21.5 | 21.5 |
| Methanol Adsorption | ≤wt% | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| Bulk Density | ≥g/ml | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.66 |
| Crushing Strength | ≤N/Pc | 30 | 80 | 30 | 80 |
| Attrition Rate | ≤wt% | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Package Moisture | ≤wt% | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
Molecular Sieve 13X APG
Description: A kind of sodium X-type aluminosilicate, with crystal diameter of 9 angstroms (0.9nm). It owns the feature of high CO2 adsorption, low regeneration temperature, and long service life.
Application
Used for general air-drying in industry, decontamination of raw material in air-separating equipment to avoid the frost tower phenomenon.
High H2O and CO2 adsorption capacity.
Specification:
| Item | Unit | Bead | Pellet | |||
| Diameter | mm | 0.5-0.8 | 1.6-2.5 | 3-5 | 1/16′ | 1/8′ |
| Static Water Adsorption | ≥wt% | 27 | 26.5 | 26.5 | 26 | 26 |
| CO2 Adsorption | ≤wt% | 17.5 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 17.5 |
| Bulk Density | ≥g/ml | 0.70 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.66 |
| Crushing Strength | ≤N/Pc | / | 25 | 70 | 25 | 65 |
| Attrition Rate | ≤wt% | / | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Package Moisture | ≤wt% | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.0 |

